1. Provide Definition of 3D topology.
Topology is the organization, flow, and structure of a vertices/edges/faces of a 3D model.
2. Name 3 types of topology
3 Sided – Tris
4 Sided – Quad
5 or more sided – N-gons
3. Name the four points that collated will make a polygonal 3D model/wireframe.
Edge, Vertex, Polygons, NURB’S
4. Find an image for each type of topology and give an explanation as to the uses of each one e.g. prons and cons.
Tris Topology: It has exactly 3 vertices at its corners and 3 edges connecting those points. This is the smallest configuration required to make a polygonal face.

Quad Topology: This is the most desired type of polygon when creating digital models, and many artists like to build their objects using nothing but quads to help make their work more appealing to customers in complex pipelines.

N-gons Topology: Due to its geometric properties, an N-Gon can always be divided into quads, tris, or a combination of the two; so they are always easy to remove by adding connecting edges between the border vertices.

5. Find an example of good topology and explain why it is good.

This is a good example of good topology as it follows how the muscles work thus giving more realistic interaction with the 3D character.
6. Find an example of bad topology and why it is bad.

This image of “Gollum” is an example of bad topology as it has lack of tension lines.
7. Give an example of when you can get away with bad topology.
You can get away with bad topology when the model is not used for complex movements or any movements at all. Because the model won’t move the awful topology won’t matter as it not gonna be seen. Or when the model is doing simple moves it won’t be easily spotted.
8. Explain why might use Polygonal Modelling.
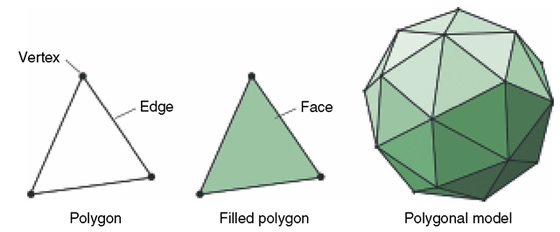
In polygonal modeling, an artist creates a digital representation of a 3D object with a geometric mesh composed of faces, edges, and vertices. Faces are usually quadrilateral or triangular and make up the surface of the 3D model. Through the use of the following techniques, a modeler methodically transforms a primitive 3D mesh (usually a cube, cylinder, or sphere) into a complete 3D model.
9. Explain why you might use NURB’s based modeling.
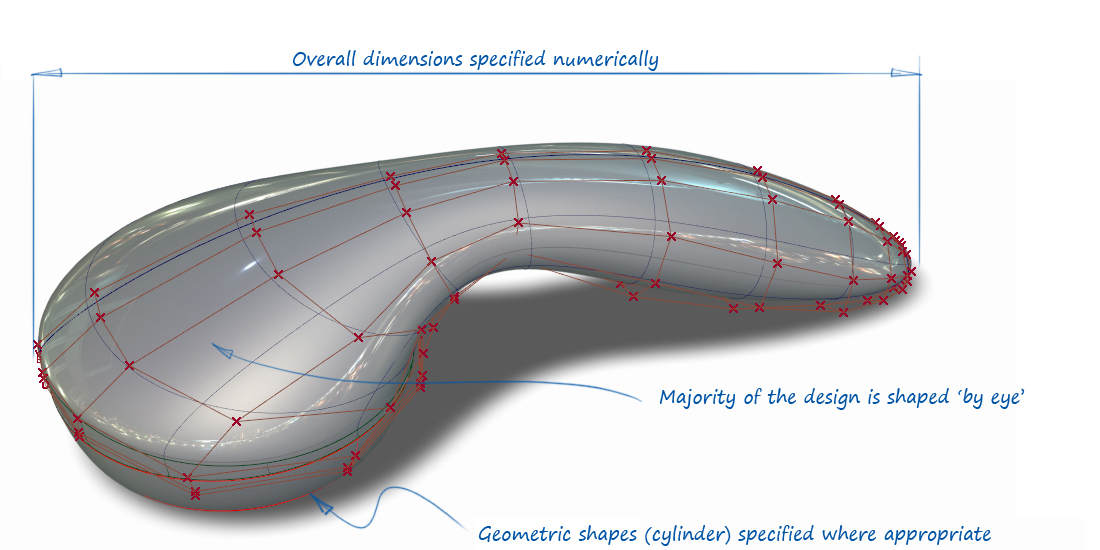
More important than the underlying math is understanding what unique features Alias NURBS has to offer you as a designer, compared to the other software tools you may be using which are, flexibility to create sculptural shapes, tension to keep surfaces smooth and taught, and alignment to create smooth invisible joins. Designing with this level of attention to sculptural aesthetics is a specialized area of CAD modeling, typically used for premium products where elegance and surface quality are important factors in the product’s appeal.
10. Explain why you might use Sub-Divisional Modelling.

This technique presupposes the division of each face into smaller faces (usually into four faces). Subdivision technique helps to add higher resolution to a 3D model. In other words, it is practically impossible to create a finished model without the smallest subdivision level.
